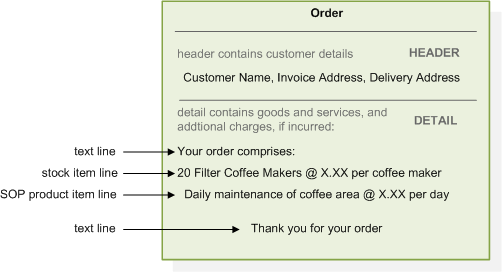
Customer orders are central to your business as a supplier. These are contractual agreements between you, the supplier, and the customer. They define the terms (prices, quantities and times) by which you will deliver products or provide services.
Strong order management allows you to maintain order visibility throughout the life cycle of an order, from demand creation to supply fulfilment. Orders may be set up individually, or as a repeat requirement for a customer so that it is produced automatically in Sage 200 on a regular basis.
|
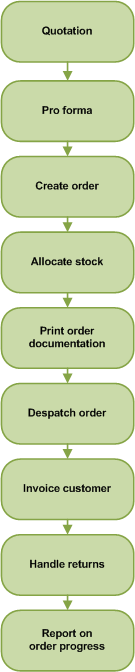
Quotation
An order may begin life as a quotation. You can track and maintain quotations and upgrade these to genuine orders. Pro forma
Where a customer requires a quotation to look like an invoice or if you require the customer to make payment before goods are despatched use the pro forma invoice. Pro forma invoice customers may become regular customers and you can upgrade the pro forma invoices to orders if this happens. Create order
Orders may be taken and created in a number of ways:
Allocate stock
Stock can be allocated during the order lifecycle. This reserves the stock held on your system, so that you can keep track of the stock levels. Once order despatch takes place, these reserved stock items are removed from the system. Print order documentation
Printing order documentation, such as picking lists, order acknowledgements and invoices, is part of the order lifecycle. Whether you choose to allow printing of these is dependent upon the settings in your system. Despatch order
Order despatch may take place immediately as in over the counter sales, or it may need to wait on stock allocation. Invoice customer
Invoices are generated to send to your customers and the invoice values are then available for posting to other modules in Sage 200 such as customers records in the Sales Ledger. If payments have been received at the point of sale, as in over the counter sales, then the payment values are posted at the same time. Handle returns
Sometimes orders are returned, and dealing with returns is another stage in the order life cycle. Report on order progress
Keeping a record of your Sales Order Processing system is important at all stages of the order life cycle. Depending on how you set up your system you might not have to complete all of the stages. For example, a quotation might never progress to a sales order. You might not need to print picking lists. You might not want order acknowledgement documentation. You might receive payment with the order (most often the case in trade counter sales). |