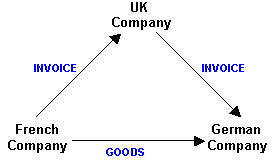
In a trading context, triangulation is the term used to describe a chain of supplies of goods and services within the EC, involving three parties. However, instead of the goods or services physically passing from one party to the other, they are delivered directly from the first to the last party in the chain.
For example:
A UK company receives an order from a customer in Germany. However, to fulfill the order the UK supplier has to purchase the goods or services from their supplier, based in France.
To save time and delivery costs, the goods or services are delivered from France to Germany but the invoice to the German customer is from the UK company.
As the goods do not enter the UK, an indicator 2 (goods) or 3 (services) is added to the EC Sales List to show that the sale was part of a triangulation transaction.
Republic of Ireland: An indicator T (goods) or S (services) is used in the EC Sales to indicate that a sale was part of a triangulation transaction.
|
|